What Best Describes a Strike-slip Fault
Ahave primarily horizontal movement. Assuming that the motion along the fault plane is pure dip-slip and that the sandstone in the hanging wall labelled as B on block X the hanging wall was connected to the sandstone of the footwall before faulting which of the following terms best describes the fault.

It S Not My Fault Engineering Design Process Engineering Design Challenge Stem For Kids
That dip-slip motion has occurred along the fault trace.

. The fault motion of a strike-slip fault is caused by shearing forces. The red line represents a fault. The San Andreas Fault is an example of a right lateral fault.
A term consisting of two components strike and. A special type of strike-slip fault B. Which of the following choices best describes what this structure is.
This problem has been solved. 113 Faults Joints. Strike-slip faults have walls that move sideways not up or down.
Imagine that you are a geologlist looking at two different folds. Normal fault Reverse fault or Strike-slip fault 12. There are two end-member varieties of faults.
Structures Formed by Brittle Deformation Sketch and briefly describe the relative motion of rock bodies located on opposite sides of normal reverse and thrust faults as well as both types of strike-slip faults. The San Andreas Fault in California is a strike-slip fault. A special type normal fault D.
Brittle fault- Normal Brittle fault StrikeSlip Ductile fold -Syncline Ductile fold Anticline Brittle fault Reverse. You observe that in the first fold the rocks get younger the farther they are away from the. Want this question answered.
Normal fault Reverse fault or Strike-slip fault 2. The figure below shows three kinds of faults. The diagram shows a cross-sectional view of a fault and layered rocks in the adjacent fault blocks.
A fault with a northwest strike. Strike-slip faults are vertical or nearly vertical fractures where the blocks have mostly moved horizontally. Strike-slip faults occur as plates scrape by each other.
That is the slip occurs along the strike not up or down the dip. Faulting geological fault fracture break fault shift - geology a crack in the earths crust resulting from the displacement of one side with respect to the other. A right-lateral strike-slip fault.
What are the different types of earthquake faults. Strike-slip fault - a geological fault in which one of the adjacent surfaces appears to have moved horizontally. The first fold is a syncline and the second is an anticline.
Inactive faults are structures that we can identify but which do no have earthquakes. See the answer See the answer See the answer done loading. ACTIVITY 21 C.
Be notified when an answer is posted. Normal fault thrust fault strike-slip fault oblique-slip faults Question 4 1 pts Which of the following best describes an anticline. Are low angle reverse faults.
If the block on the far side of the fault moves to the left as shown in this animation the fault is called left-lateral. Two fault blocks move in the same direction. If the block opposite an observer looking across the fault moves to the right the slip style is termed right lateral.
900 1000 900 1100 1200 -1000 900 800 200 m 700 1 You are given some information regarding the attitudes of the coal seam and the fault. The beds are inclined dip away from the fold axis central part of the fold The oldest layers found in the midd le of the fold are Many anticlilnes are asymmetric and some may have. Strike-slip fault - a fault on which the two blocks slide past one another.
In this specific fault the. FAULTS Identify the type of fault seen on the following pictures 1. One fault block moves down relative to the other.
Choose the statement that best describes a thrust fault. A unique fault in which the fault plane is vertical C. They built it right over a geological fault.
Complete the table below. Which of these statements best describes a strike-slip fault. The displacement along a strike-slip fault is _____ to the strike of the fault.
To step back a bit strike-slip faults are how geoscientists describe the motion of two plates in contact with one another. Which of these statements best describes a strike-slip fault. The San Andreas Fault in California is a strike-slip fault.
Which of the following can form as a result of tension by tectonic plate movement. If the block opposite an observer looking across the fault moves to the right the slip style is termed right-lateral. The orientation of a plane in space is expressed by its attitude.
A left-lateral strike-slip fault is one on which the displacement of the far block is to the left when viewed from either side. Which of these answers best describes compression caused by tectonic plate movement. Transform transcurrent fault lateral fault tear fault or wrench fault.
Strike-slip faults are vertical or nearly vertical fractures where the blocks have mostly moved horizontally. 10 points Strike True dip Coal seam 23 Fault 74 2 If drawing a cross-section from X to Y what are the apparent dips for the coal seam and the. Offset of a linear feature the line of trees.
A special type of reverse fault. Have no appreciable displacement. In these faults the fault plane is usually vertical so there is no hanging wall or footwall.
Have primarily vertical movement. If the block moves to the left the motion is termed left lateral. Where is the best studied strike slip fault.
If the block on the far side moves to the right the fault is called right-lateral Other names. 5When oceanic or continental plates slide past each other in opposite directions or move in the same direction but at different speeds anticline transform fault. One fault block moves up relative to the other.
Name the type of fault from the diagram below.

Earthquake Faults 3 Basic Types In Brief Educational Youtube

Schematic Of A Releasing Bend In A Left Lateral Strike Slip Fault The Download Scientific Diagram

Co Seismic Strike Slip Fault Displacement Determined From Push Up Structures The Selsund Fault Case South Iceland Sciencedirect

Fault Parts Types Field Evidences

Global Catalogue Classification And Tectonic Origins Of Restraining And Releasing Bends On Active And Ancient Strike Slip Fault Systems Geological Society London Special Publications

Strike Slip Fault Definition Examples Locations Britannica
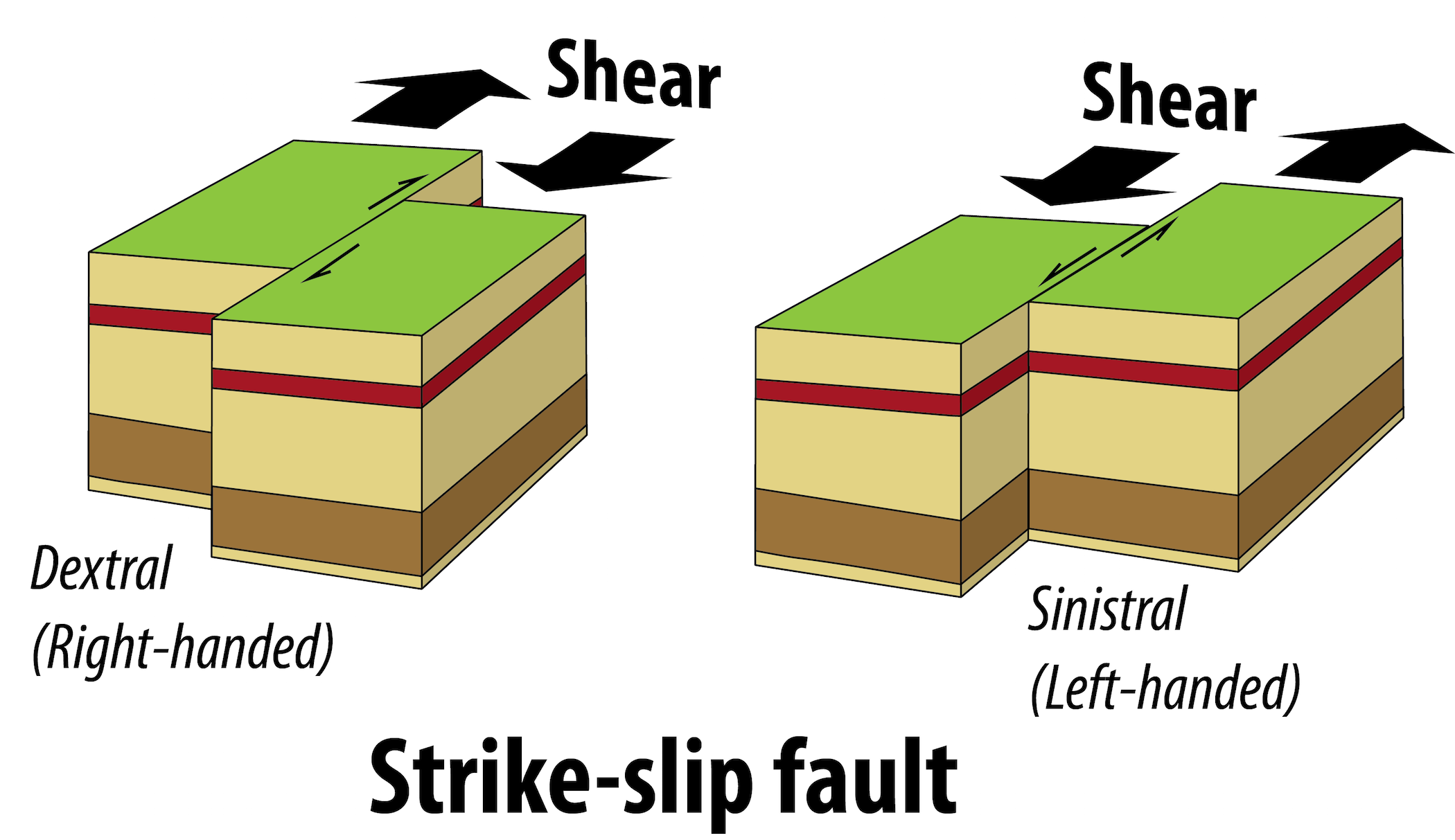
13 3 Fractures Joints And Faults Physical Geology First University Of Saskatchewan Edition

Schematic Of A Releasing Bend In A Left Lateral Strike Slip Fault The Download Scientific Diagram

Faulting Folding Foam Faults Demo Incorporated Research Institutions For Seismology

Strike Slip Fault Definition Examples Locations Britannica
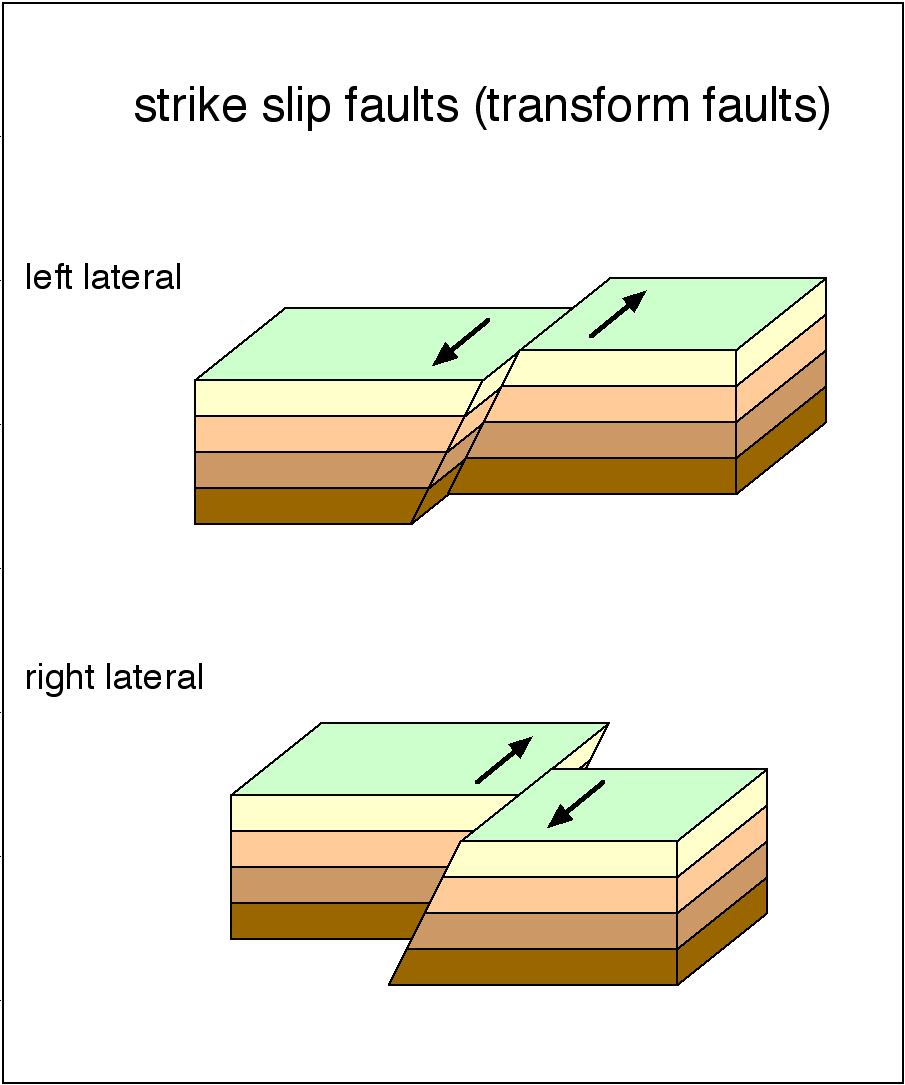
Information And Resources About The San Andreas Fault
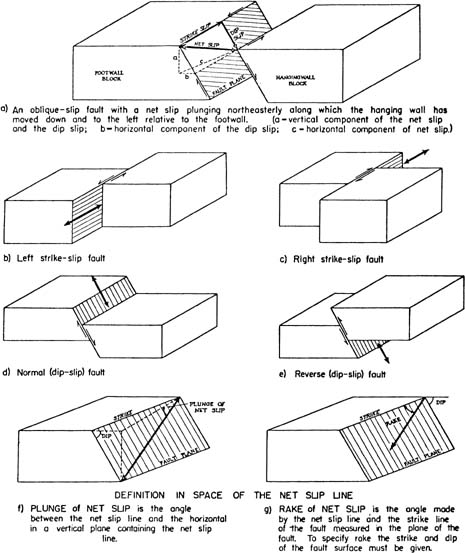
Faults And Faulting Springerlink

Co Seismic Strike Slip Fault Displacement Determined From Push Up Structures The Selsund Fault Case South Iceland Sciencedirect
Lecture 3 Joints Fractures And Faults

Strike Slip Fault Definition Examples Locations Geology Britannica Slip
12 3 Fracturing And Faulting Physical Geology
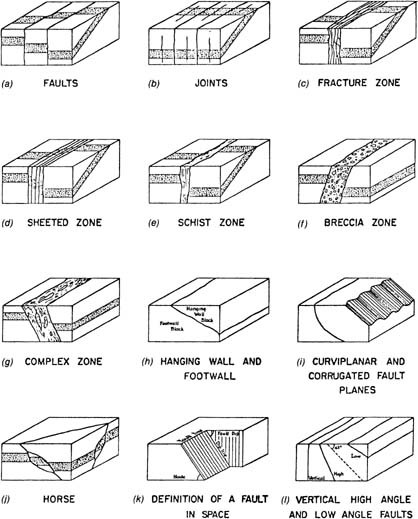
Faults And Faulting Springerlink

Scheme Of Geometric Relationship Between Nnw Sse Strike Slip Fault Download Scientific Diagram

Comments
Post a Comment